Build Your Own Port Scanner.

*** Do not Use againts any Hosts Without Proper Authorization***
What is a Port Scanner ?
A port scanner is a computer program or tool used to scan and identify open ports on a computer or network device. Ports are numbered endpoints for network connections, and they allow different services or applications to communicate over a network. Port scanning is a technique used for various purposes, including network security assessment, troubleshooting, and system administration.
Lets Build Our Own :D
Lets Start with Importing Necessary Modules
import sys
import socket
import ipaddress
from datetime import datetime
Ip Validation Function , if the ip_address funtion throws a ValueError that means the Entered Ip is Incorrect.
def validate_ip(ip):
try:
ipaddress.ip_address(ip)
return True
except ValueError:
return False
Scan_ip Function Takes 2 arguements
Target Ip and Scan Type , 1 To Scan all 65535 Ports and 2
to Scan first Common 1000 Ports .
The built-in python socket library has this connect_ex() function returns 0 if the operation is
successful otherwise will return a value to errno variable. What this means is if the connection
is successful the method connect_ex() returns 0 otherwise some value will be returned.Which
Tells us if the Port is open or not.
def scan_ip(target, r):
try:
if r == 1:
x = 0
y = 65565
elif r == 2:
x = 0
y = 1023
else:
print("Please Select Correct Scan Option")
#Banner
print("-"*50)
print(f"Scanning Target :{target}")
print(f"Time Started: {str(datetime.now())}")
print("-"*50)
for port in range(x, y):
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
socket.setdefaulttimeout(1)
result = s.connect_ex((target, port))
if result == 0:
print(f"Port :{port} is Opened")
s.close()
#Banner
print("-"*50)
print("Scan Completed")
print("-"*50)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("\n Exiting Program")
sys.exit()
except socket.gaierror:
print("Hostname could not be Resolved.")
sys.exit()
except socket.error:
print("could Not Connect to the server")Next We are just checking if the User has entered two Command Line Arguements And Set the Target to Entered IP , and Fire the scan_ip function.
if len(sys.argv) == 2 and validate_ip(sys.argv[1]):
target = socket.gethostbyname(sys.argv[1])
print("Scan Options.......")
print("1 : Scan All Ports")
print("2 : Scan Common Ports")
r = int(input("Enter Scan Option :"))
scan_ip(target, r)
else:
print("Invalid Syntax")
print(" try PortScan.py <ip> ")And now lets see how it worked ...
Im Testing This on my Default Gateway Router which I know is running a Web page
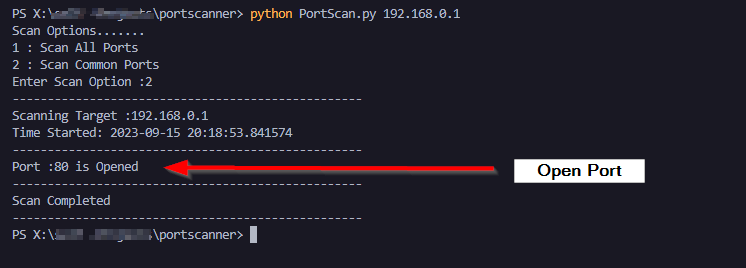
Alright , Now we Have Created Our Very Own Port Scanner.